There has been widespread speculation that the dollar will eventually be replaced as the reserve currency. Diversification continues perpetuating as countries try to balance the volumes of currency they hold at central banks. News that China would begin to use the Yuan to trade energy products is an example of countries looking for a common currency other than the US dollar to become part of their total reserves. While there could be continued diversification, even into cryptocurrencies to some extent replacing the dollar as the only reserve in a central bank pool, it would take a giant leap for countries to move away from the greenback as the world’s reserve currency. About 60 per cent of the world’s reserves are held in US dollars.
Why does the dollar have such a tight grip?
The dollar has been the reserve currency and has ruled the financial world for about 80 years since the end of World War II. The dollar has embedded itself into good and services trade, and nearly all commodities are quoted in US dollars. Commodities include most of the raw materials used to build, move, and eat. For example, Aluminum and steel are used to construct buildings, cars, and planes. Oil is used to make gasoline to drive our cars and trucks.
Corn and wheat are used to make flour and bread and feed most farm animals. The dollar has become ingrained in the global trade of commodities, where the dollar’s movements can impact the direction of most commodities. For example, when the dollar moves higher, it becomes more expensive for countries in Europe and Asia to purchase oil as the value of oil in dollar terms has become more expensive. When Russia sells oil to the EU, it does so into a dollar account, which needs to be converted into Euros.
How did the dollar wrestle control and stay the king
Post World War II, there was a concerted effort to repair the global economy. The Bretton Woods meeting in New Hampshire had representatives of 44 nations intending to find a way to stabilize and expand economic growth. It was agreed that countries would use the dollar as a bench and fix the dollar’s value to gold and other countries would fix their currencies to the dollar. Instead of holding gold in reserves, countries now had to hold dollars in reserve. By holding dollars, each country would be able to maintain its exchange rate. This agreement allowed the dollar to become the dominant currency.
Eventually, the Bretton Woods agreement collapsed because of the lack of gold available to continue fixing the US. Still, the dollar was deeply entrenched as the reserve currency and could not easily be replaced by an alternative. The United States currency was attractive because of its regulatory framework, transparency, and flexible and substantial capital markets environment. The United States economic framework allowed the dollar to remain dominant even though countries no longer needed to peg their currencies to the greenback.
Why are countries now looking for alternatives
The reserve currency has become an issue again since the invasion of Ukraine by Russia in 2022. The attack led to a deluge of sanctions by the United States that were geared to impact Russia financially. The most prominent was the decision to freeze about $300 billion of Russian foreign currency reserve and terminate Russian banks from SWIFT.
What is SWIFT
SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) is a global financial messaging network banks and other financial institutions use to securely transmit information and instructions through a standardized system of codes. It is used to facilitate international money transfers between banks and other financial institutions and is the most widely used system for international money transfers. Banks worldwide will use SWIFT to send instructions to pay or receive money for several reasons, including oil purchases.
How did removal from SWIFT impact Russia?
The removal of Russia from the SWIFT system has significantly impacted the country’s economy. It has made it more difficult for Russian banks to access international financial markets, as they can no longer use the SWIFT system to transfer money. This situation has resulted in a decrease in foreign investment and a reduction in the value of the Russian ruble. Additionally, it has made it more difficult for Russian businesses to conduct international transactions, as they can now not use the SWIFT system to transfer money.
Russia called the financial tactics used by the United States in the wake of the attack a weaponization of the dollar. Those who relied on Russian oil that did not want to punish Russia for finding an alternative source of oil, like China, were forced to promote an alternative financial infrastructure.
Who else is concerned about dollar as a reserve currency
It’s not only Russia and China who are concerned about the power of the dollar and the United States’ ability to use sanctions to terminate trade. Argentina and Brazil, along with areas of the Middle East and South East Asia, are concerned that someday the United States will use the power of its currency to target their nations the way it targeted Russia.
Has the dollar lost some cash
There has been some loss in reserve holdings despite the current loft level of 60 per cent of the total currency reserve. In 2000, the dollar was held by 70 per cent of the total global currency reserve. The Euro has taken a small market share but has only increased from 18 per cent of total world reserves to 20 per cent since its inception. The Chinese Yuan has grown the fastest in several years, but only 3 per cent of total reserves are held in Yuan.
China is also in the process of winding down its US reserves. To hold dollars, China has purchased and is one of the largest holders of US Treasury Bonds. According to Aljazeera, China holds $870 billion in US debt obligations. The total holdings are the lowest China has held since 2010. China is also attempting to negotiate a transaction in Yuan instead of dollars. In February 2022, Iraq and China announced they would trade for a settlement in Yuan. Following the removal of its banks from SWIFT, Russia has also decided to hold all of its gas and oil surplus revenue in 2023 in Chinese Yuan.
Another issue is the value of the dollar and the cost to pay the dollar-denominated debt. Firstly, US interest rates have increased from zero to 5 per cent since March 2022. Not only have rates in the US outpaced other counties, but there continues to be the belief by market participants that US rates will continue to rise. According to the CME Fed Tool, the expectation is that there will be a rate hike in July, followed by higher rates for longer for the balance of 2023.
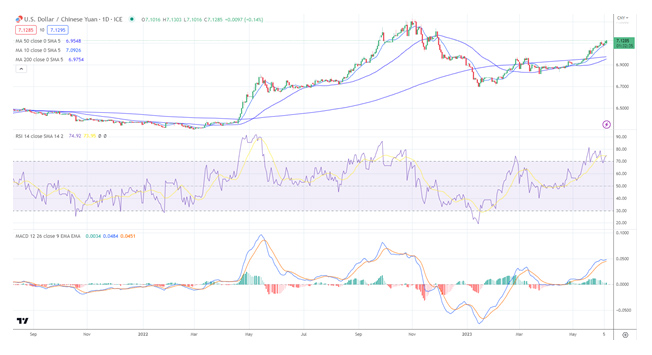
The dollar has rallied in the forex market versus the Chinese Yuan. In June 2023, it hit a high for the year and continued rising as the interest rate differential made the dollar more attractive. The 50-day moving average is poised to exceed the 200-day moving average, which means a long-term up trend is in place. This scenario is called a ‘golden cross’. A golden cross trading strategy is a technical analysis strategy that involves buying the USD/CNY when its short-term moving average exceeds its long-term moving average. This bullish scenario indicates that the USD/CNY will likely experience an upward trend soon.
The bottom line
The dollar is unlikely to be replaced by another currency as the reserve currency for the global economy. Recall the dollar was able to gain its prominence in the wake of World War II. The US at the time was the world’s largest economy and was trusted by the rest of the world because of its regulatory framework and financial flexibility.
Fast forward to today, and many countries do not like what they have recently seen from the United States. While the regulatory framework is intact, there is fear that you will become financially insolvent if the US turns on your country. Following the attack on Ukraine by Russia, the United States used its financial might to sanction Russia and take them off the SWIFT payment processing system. Without instructions from SWIFT, Russia could not participate in financial activities and needed to develop a new way to provide commerce with countries that traded with Russia. China and India are two large countries that continue to purchase oil from Russia.
While China, Russia, and a few other countries are concerned about what the United States can do to an economy, they are in the minority. Approximately 60 per cent of the world’s currency reserves are in US dollars. This figure compares to about 20 per cent for Europe. While there is a slow decline in the percentage of reserves held in dollars, the US currency will likely remain king for the foreseeable future.