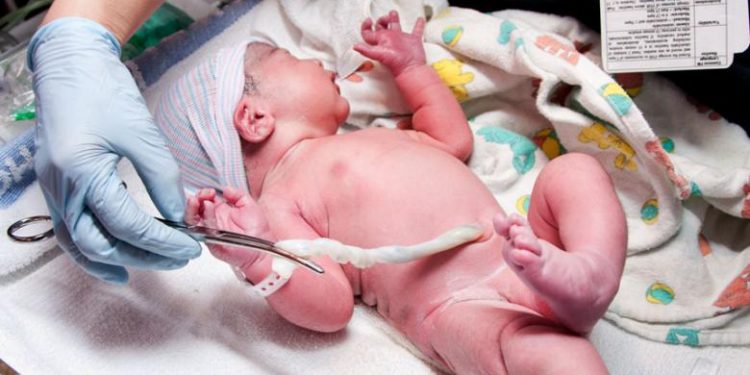
The umbilical cord plays a vital role in developing baby during gestation period. The formation of the umbilical cord occurs between the fourth and eighth week of gestation. It forms a connection between the mother’s placenta and the fetus.
After the birth of a baby, doctors cut its cord so that the baby can breathe on its own. After birth, the cord is clamped and after some days, it gets dried and detached.
Doctors generally advise parents to preserve the dried cord because the cord blood is essential. Cord blood is the blood left in the umbilical cord after birth. It contains stem cells. These cells have the amazing ability to grow into many different kinds of cells, like bone marrow cells, blood cells, or brain cells. This can make them valuable for treating some diseases like leukemia, Hodgkin’s disease, and some types of anemia.
The cord blood is sent to placenta bank for its preserve. It is preserved in minus 196 degree centigrade with the help of liquid nitrogen. This can be saved for 600 years. This is called as master stem cells. These master stem cells are capable of developing 200 human cells. When these master stem cells are transplanted into a child who is ill, those cells can grow new bone marrow cells to replace the ones destroyed by the disease or its treatment.
These master cells are also helpful in research of hereditary diseases, some health experts observe.
PNN/Agencies