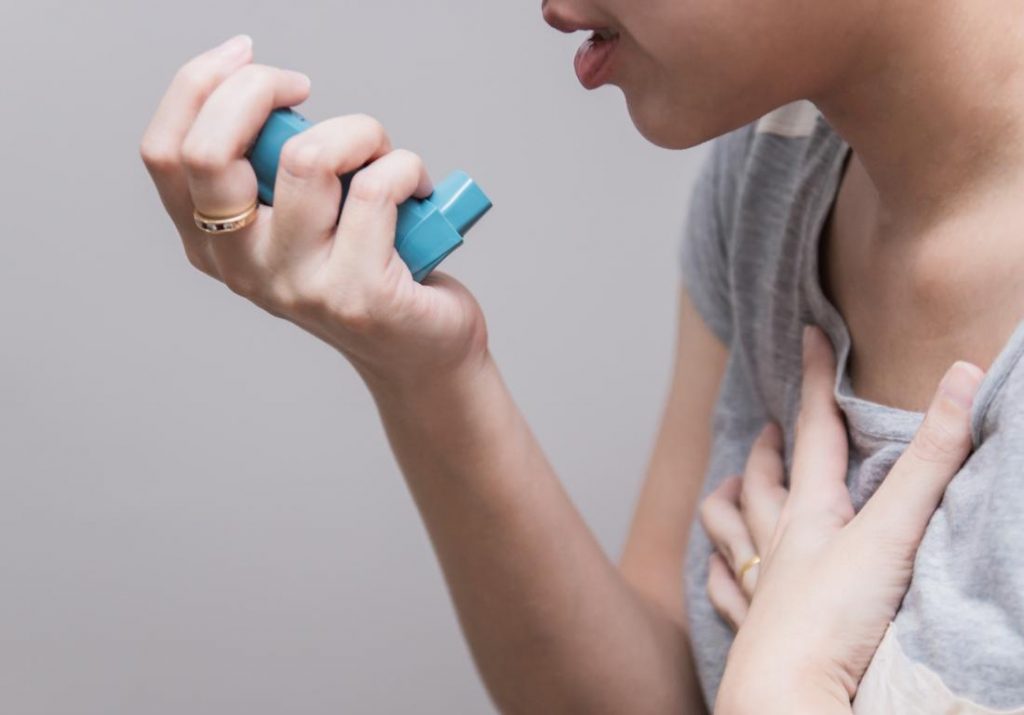
Sydney: Out-of-pocket costs are preventing many people from taking vital asthma medication, says a new study, calling for urgent interventions to promote discussions between patients and doctors about the cost of medicines to treat asthma.
The most commonly prescribed preventer treatments for asthma contain inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) which, if taken regularly, reduce the severity of the disease and the number of asthma-related deaths, said the researchers.
According to reports, at least one in every 10 asthma patient globally lives in India and the economic costs associated with asthma exceed those of TB and HIV/AIDS combined.
To reach this conclusion, researchers led by The George Institute for Global Health and the Woolcock Institute of Medical Research at UNSW Sydney, surveyed 1,400 people with asthma in Australia and found that half of the adults and one-third of the children in the study were either decreasing or skipping doses of asthma medicines to make them last longer.
“We know that preventer inhalers can be incredibly effective at controlling symptoms and preventing people from being hospitalised or even from dying of asthma, yet our study has found that out-of-pocket costs are preventing many from accessing medicines which can be life-saving,” said senior research fellow Tracey-Lea Laba of The George Institute.
The study found that young male adults were the most likely to under-use asthma treatments.
This was compounded by doctors being largely unaware that out-of-pocket costs were a significant concern for many of their patients, or that some preventers had lower out-of-pocket costs for patients than others.
According to fellow study author Professor Helen Reddel of the Woolcock Institute at UNSW Sydney, asthma is a long-term disease and one where people really need to keep the inflammation under control by taking a preventative medicine and not just relying on short-term symptom relief from a blue inhaler.
“We need doctors to talk to their patients to stress that this Band-Aid approach does not work, and can leave them hospitalised or even worse as a result,” said Reddel.
The results were published in the journal JACI : In Practice.
IANS